Scope Tab¶
The Scope is a powerful time domain and frequency domain measurement tool as introduced in Unique Set of Analysis Tools and is available on all HF2 Series instruments.
Features¶
- One input channel with 2 kSa of memory
- 14 bit nominal resolution
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT): up to 100 MHz span, spectral density and power conversion, choice of window functions
- Sampling rates from 6.4 kSa/s to 210 MSa/s; up to 10 μs acquisition time at 210 MSa/s or 320 ms at 6.4 kSa/s
- 4 signal sources; up to 13 trigger sources and 2 trigger methods `
- Independent hold-off and trigger level settings
Description¶
The Scope tab serves as the graphical display for time domain data. Whenever the tab is closed or an additional one of the same type is needed, clicking the following icon will open a new instance of the tab.
| Control/Tool | Option/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Displays shots of data samples in time and frequency domain (FFT) representation. |
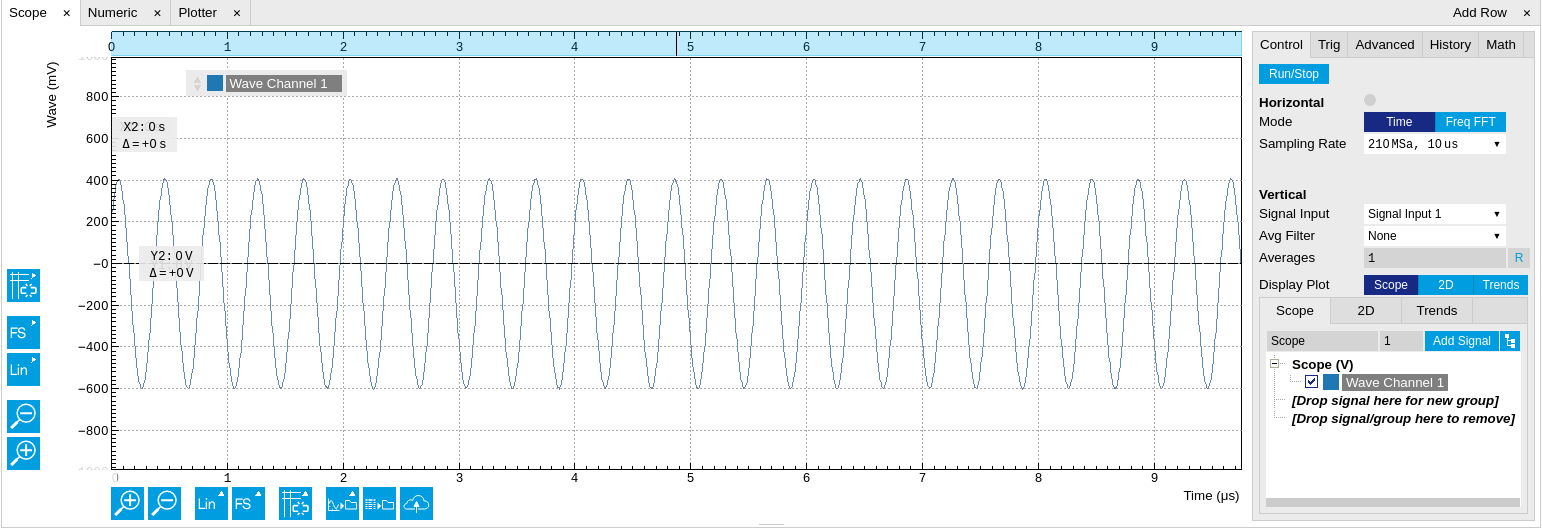
The Scope tab consists of a plot section on the left and a configuration section on the right. The configuration section is further divided into a number of sub-tabs. It gives access to a single-channel oscilloscope that can be used to monitor a choice of signals in the time or frequency domain. Hence the X axis of the plot area is time (for time domain display, Figure 1) or frequency (for frequency domain display, Figure 3). It is possible to display the time trace and the associated FFT simultaneously by opening a second instance of the Scope tab.
The Scope records data from a single channel at up to 210 MSa/s. The channel can be selected among the two Signal Inputs and the two Signal Outputs. The Scope records data sets of up to 2 kSa samples in the standard configuration, which corresponds to an acquisition time of 10 μs at the highest sampling rate.

The frequency domain representation is activated in the Control sub-tab by selecting Freq Domain FFT as the Horizontal Mode. It allows the user to observe the spectrum of the acquired shots of samples. All controls and settings are shared between the time domain and frequency domain representations.
The Scope supports averaging over multiple shots. The functionality is implemented by means of an exponential moving average filter with configurable filter depth. Averaging helps to suppress noise components that are uncorrelated with the main signal. It is particularly useful in combination with the Frequency Domain FFT mode where it can help to reveal harmonic signals and disturbances that might otherwise be hidden below the noise floor.
The Trigger sub-tab offers all the controls necessary for triggering on different signal sources. When the trigger is enabled, then oscilloscope shots are acquired whenever the trigger conditions are met. Trigger and Hysteresis levels can be indicated graphically in the plot. A disabled trigger is equivalent to continuous oscilloscope shot acquisition.
Functional Elements¶
For the Vertical Axis Groups, please see the table "Vertical Axis Groups description" in the section called "Vertical Axis Groups".
| Control/Tool | Option/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger | grey/green/yellow | When flashing, indicates that new scope shots are being captured and displayed in the plot area. The Trigger must not necessarily be enabled for this indicator to flash. A disabled trigger is equivalent to continuous acquisition. Scope shots with data loss are indicated by yellow. Such an invalid scope shot is not processed. |
| Signal | Selects the trigger source signal. | |
| Off | Switches the scope off. | |
| Continuous | A new waveform is acquired and displayed after the hold off time. The trigger source is ignored. | |
| Signal Inputs 1/2 | A new waveform is acquired and displayed when the respective Signal Input is matching the trigger condition. | |
| Signal Outputs 1/2 | A new waveform is acquired and displayed when the respective Signal Output is matching the trigger condition. | |
| Oscillators 1-8 | A new waveform is acquired and displayed when the respective Oscillator is matching the trigger condition. | |
| DIO 0/1 | A new waveform is acquired and displayed when the respective DIO signal is matching the trigger condition. | |
| Slope | Falling edge trigger | Select the signal edge that should activate the trigger. |
| Rising edge trigger | ||
| Level (%) | numeric percentage value (negative values permitted) | Defines the trigger level relative to signal full scale. |
| Holdoff (s) | numeric value | Defines the time before the trigger is rearmed after a recording event. |
| Plot Type | Select the plot type. | |
| None | No plot displayed. | |
| 2D | Display defined number of grid rows as one 2D plot. | |
| Row | Display only the trace of index defined in the Active Row field. | |
| 2D + Row | Display 2D and row plots. | |
| Active Row | integer value | Set the row index to be displayed in the Row plot. |
| Track Active Row | ON / OFF | If enabled, the active row marker will track with the last recorded row. The active row control field is read-only if enabled. |
| Palette | Solar | Select the colormap for the current plot. |
| Viridis | ||
| Inferno | ||
| Balance | ||
| Turbo | ||
| Grey | ||
| Colorscale | ON / OFF | Enable/disable the colorscale bar display in the 2D plot. |
| Mapping | Mapping of colorscale. | |
| Lin | Enable linear mapping. | |
| Log | Enable logarithmic mapping. | |
| dB | Enable logarithmic mapping in dB. | |
| Scaling | Full Scale/Manual/Auto | Scaling of colorscale. |
| Clamp To Color | ON / OFF | When enabled, grid values that are outside of defined Min or Max region are painted with Min or Max color equivalents. When disabled, Grid values that are outside of defined Min or Max values are left transparent. |
| Start | numeric value | Lower limit of colorscale. Only visible for manual scaling. |
| Stop | numeric value | Upper limit of colorscale. Only visible for manual scaling. |
| Control/Tool | Option/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FFT Window | Cosine squared (ring-down) | Several different FFT windows to choose from. Each window function results in a different trade-off between amplitude accuracy and spectral leakage. Please check the literature to find the window function that best suits your needs. |
| Rectangular | ||
| Hann | ||
| Hamming | ||
| Blackman Harris | ||
| Flat Top | ||
| Exponential (ring-down) | ||
| Cosine (ring-down) | ||
| Resolution (Hz) | mHz to Hz | Spectral resolution defined by the reciprocal acquisition time (sample rate, number of samples recorded). |
| Correction | ON / OFF | When Power is selected, it applies power correction to the spectrum to compensate for the shift that the window function causes. Power correction is useful for noise measurements to correct the noise floor. When Amp is selected, amplitude compensation is applied which corrects the peak amplitudes of coherent tones. |
| Absolute Frequency | ON / OFF | Shifts x-axis labeling to show the absolute frequency in the center as opposed to 0 Hz, when turned off. |
| Spectral Density | ON / OFF | Calculate and show the spectral density. If power is enabled the power spectral density value is calculated. The spectral density is used to analyze noise. |
| Power | ON / OFF | Calculate and show the power value. To extract power spectral density (PSD) this button should be enabled together with Spectral Density. |
| Persistence | ON / OFF | Keeps previous scope shots in the display. The color scheme visualizes the number of occurrences at certain positions in time and amplitude by a multi-color scheme. |
| BW Limit | Selects between sample decimation and sample averaging. Averaging avoids aliasing, but may conceal signal peaks. | |
| OFF | Selects sample decimation for sample rates lower than the maximal available sampling rate. | |
| ON | Selects sample averaging for sample rates lower than the maximal available sampling rate. | |
| Rate | Streaming rate of the scope channels. The streaming rate can be adjusted independent from the scope sampling rate. The maximum rate depends on the interface used for transfer. Note: scope streaming requires the DIG option. |
For the Math sub-tab please see the table "Plot math description" in the section called "Cursors and Math".



