DIO Tab¶
The DIO tab provides access to the settings and controls of the digital inputs and outputs. It is available on all SHFQA+ Instruments.
Features¶
- Monitor and control of 32-bit DIO port
- Communicate qubit states via 32-bit DIO port
- Configure Trigger Inputs and Marker Outputs
Description¶
The DIO tab is the main panel to control the digital inputs and outputs as well as the trigger levels. Whenever the tab is closed or an additional one of the same type is needed, clicking the following icon will open a new instance of the tab.
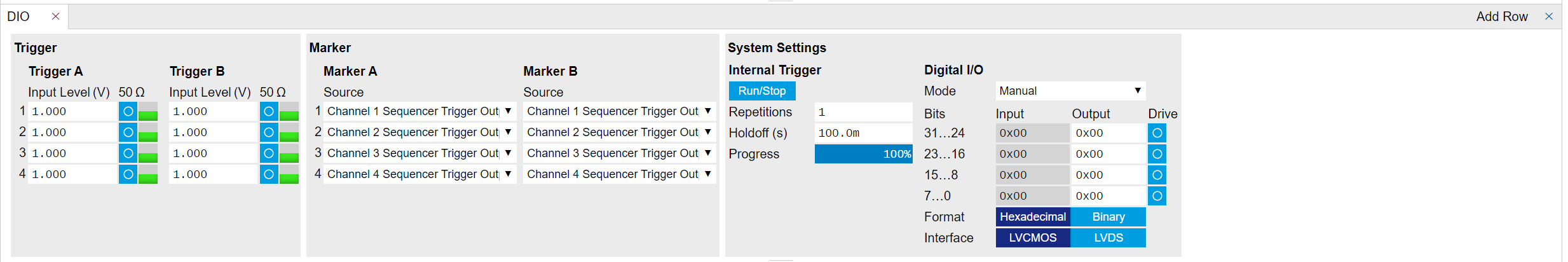
The DIO tab includes 3 sub-tabs: Trigger for configuration of trigger input level and impedance, and monitor of trigger input status on the front panel; Marker for configuration of marker source sending out from the front panel; System Settings for configuration of the internal trigger, and the 32-bit Digital I/O ports on the back panel detailed in the next section.
Digital I/O¶
Figure 2 shows the architecture of the DIO port. It features 32 bits that can be configured byte-wise as inputs or outputs. Even when a byte is configured as output, it works as input as well and can be read. The digital output data is synchronous to an internal clock, which is running at 50 MHz.

The DIO interface specification is detailed in the Specifications.
The Digital I/O has 3 operation modes:
-
In Manual mode, each DIO pin can be controlled manually from the UI or the API
-
In QA Sequencer N mode, each DIO pin output can be controlled by the Readout Pulse Generator Sequencer N (N indicates which Channel) with a SeqC instruction
setDIO -
In QA Results QCCS mode, DIO pins are configured to send Readout Result after Thresholding. Table 2 shows the mapping between DIO pins and input/output signals available when using the DIO connector to output qubit state measurement results. The direction is as seen from the SHFQA+ Instrument. In order to use these signals, the Digital I/O Mode and Drive setting have to be chosen accordingly.
| DIOLink signal | DIO pin | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| VALID | DIO[0] | OUT | valid bit |
| CW | DIO[4:1] | OUT | one-hot encoding of Readout Channel |
| CW | DIO[8:23] | OUT | quantized results for a maximum of 16 State Discriminations |
| reserved | DIO[24:31] | IN | incoming communication |
Figure 3 below shows an example of multiple channel readout transmissions through DIO. Every readout is sent in a single message. A one-hot encoding of the readout channel is sent along with the readout on dedicated bits. The valid bit is set for every valid DIO transaction.

The QA Results QCCS mode of the DIO interface provides one way of communicating discriminated qubit states between 2 Instruments. For more than 2 Instruments, both qubit states and synchronization becomes essential. The following section explains how the ZSync interface works for both Instrument synchronization and feedback. Please note that ZSync settings are under the Device Tab.
ZSync Interface¶
The ZSync link of the Zurich Instruments' Quantum Computing Control System (QCCS) enables Instrument synchronization and communication on the system level through the Zurich Instruments' PQSC Programmable Quantum System Controller. This architecture is able to support quantum algorithms run in scalable quantum processors.
In particular, the ZSync links distribute the system clock to all Instruments and synchronize all Instruments to sub-nanosecond levels. Besides status monitoring to ensure quality and reliability of qubit tune-up routines, it provides a bidirectional data interface to send readout results to, or obtain sequence instructions from the PQSC.
The ZSync links adhere to strict real-time behavior: all data transfers are predictable to single clock cycle precision. In the SHFQA+, the link is optimized for maximum data transfer bandwidth to the central controller. For example, twice the bandwidth is reserved for results being transferred to the PQSC with respect to the allocated bandwidth for instructions that are received from the PQSC. This enables global feedback and error correction through centralized syndrome decoding and synchronized actions on the global QCCS system level.
Feedback through the PQSC¶
Note
More information on the ZSync, and how to properly link the SHFQA+ with the QCCS can be found in the user manual of the PQSC Programmable Quantum System Controller.
When using the startQA command, the SHFQA+ generates a readout result and forwards it to the PQSC over
the ZSync interface. The PQSC stores it in the
register bank, which handles and distributes feedback information in the QCCS system. Depending on the PQSC configuration, the results are forwarded to other devices in the
QCCS, such as the SHFSG+.
To tell the PQSC how it should forward or process the readout results, the SHFQA+ sends some additional information before the readout results:
- An Address that tells the PQSC which register of the Readout Register Bank the readout results should be directed to. This is the parameter
addressof thestartQAcommand. - An Integrators mask that indicates which integration units were activated in this readout. This is the
weighted_integrator_maskof thestartQAcommand. When Multi State Discrimination is active, the integration mask reflects the multi-state assignment.
Each component is sent in a separate ZSync message. The address is sent first, followed by the Integrators mask, and then the readout results, see Figure 4. To reduce latency, the address and the mask are sent while the readout measurement is being performed, and the readout results are then sent as soon as the discriminated qubit readout results are ready.
The readout results are sent before any averaging, so the PQSC will receive the single readout shots and not the averaged values.

Because the SHFQA+ has multiple channels, the forwarding of the readout results is interleaved to reduce latency. For example, if two readout channels perform a readout at the same time, the SHFQA+ first sends the addresses and integrator masks for both channels at the beginning of the integration. Then, it sends the readout results interleaved as soon as they are available. The order is given by the index of the QA Channel, so channel 1 goes first and so on.

If the QA Channels are not started at the same exact time, the data from the channels that start later are sent only once the data being processed are fully sent:

